LGSF Technology
What Is Cellular Concrete?
Cellular concrete is a lightweight, flowable cement-based material filled with air bubbles. It offers good thermal insulation, load distribution, and speed in construction.
Why Combine LGSF with Cellular Concrete?
- Faster Installation: Cellular concrete raft foundations cure quickly.
- Dry Construction: No bricklaying, less water usage.
- Seismic Resilience: LGSF + Cellular base absorb earthquake shocks.
- Thermal & Acoustic Insulation: Multi-layered wall systems + insulated foundation.
- Lightweight Yet Strong: Perfect for modular, transportable housing.
Structural Specifications
- Foundation: 200mm Cellular Concrete Raft + 100–150mm RCC Slab
- Wall: Steel Framing with Fiber Cement or ACP Panels
- Insulation: Between studs – Glass wool or similar
- Roof: Galvalume or PUF Panel
- Finishing: Gypboard interior, weather-resistant exterior
Compared To Traditional Construction
- 50% faster completion
- No heavy formwork or brick masonry
- Lower seismic load
- Better insulation
- Ideal for remote, hilly, or fast-track areas
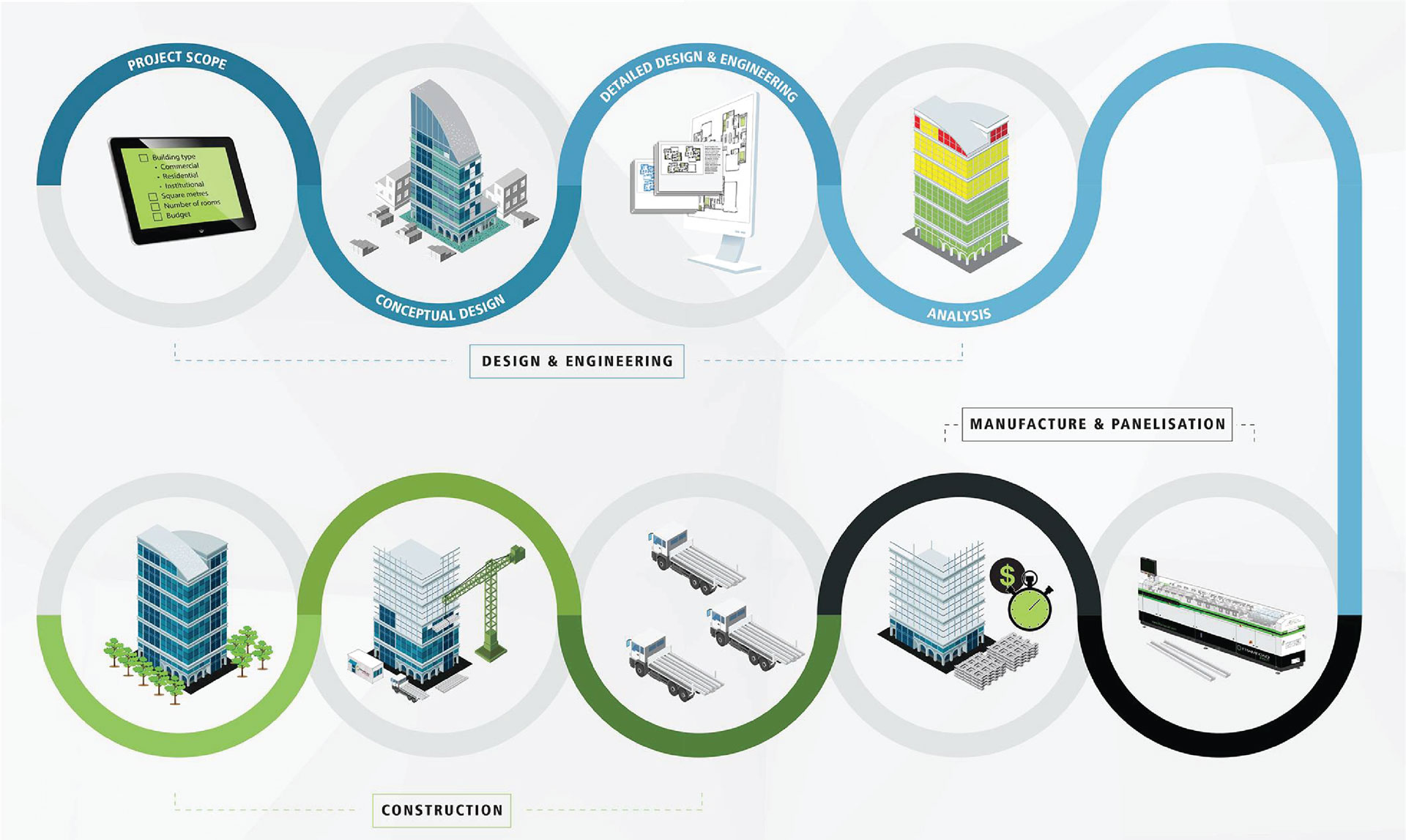
LGSF High-precision, Sustainable, And Fast Construction
LGSF is a construction technology using cold-formed steel produced by highly advanced and precise machinery. This method is highly efficient and can be adopted to practically any building type. It is also environmentally sustainable and produces a strong, high performing structure.
Delivering Simplicity Light Gauge Steel Framing (LGSF) Prefab Building Technology
Ideal alternative construction technology for:
Hotels and resorts
Rooftop extensions
Farmhouse or mountain retreat
Pods and cabins
Commercial buildings
Portable structures
Hospitals, schools & colleges
Warehouses
LGSF Technical Specifications
LGSF Delivers
- A viable alternative to traditional construction
- Fast and predictable outcomes
- Energy efficient and environmentally friendly
LGSF Design
- Profiles: 89mm / 150mm (Thk 0.7 to 2.0mm)
- Configurations: 100% LGSF or HR/LGSF Hybrid
Wall Cladding
- Fiber Cement Board / Planks
- Cement Particle Board (Bison)
- Knuf Aquapanel
- Aluminium Composite Panel (ACP)
- Various other cladding options
Roof Options
- Fiber Cement & Galvalume/Shingles
- PUF Sandwiched panel
- Decking with concrete
Floor Options
- Floor joists and decking sheet with concrete
- Fiber cement board (18 or 24mm)
Insulation
- Rockwool Insulation
- Glasswool Insulation
- High thermal efficiency
Advantages
-
Faster Construction
upto 50% savings in time -
Long building life
uses galvanized steel -
Environmentally friendly
-
Dry Construction
does not use water -
Better thermal performance
by using insulating material
LGSF Suitable Building Types
G+3 buildings can be constructed using 100% Light Gauge Frames, additional floors can be constructed using a hybrid HR/CR construction.
-
Office / Commercial buildings
-
Residential
-
Modular / Pods
-
Industrial - Other
Comparison with conventional construction
G+3 buildings can be constructed using 100% Light Gauge Frames, additional floors can be constructed using a hybrid HR/CR construction.
| Brick & RCC Construction | LGSF Construction |
|---|---|
| Quality of construction varies as materials sourced from different vendors. | All materials are of uniform quality. |
| Huge transportation costs as all materials are heavy. | Huge savings in transportation costs as LGSF construction is 1/10th weight of that of brick wall. |
| Uneven surface requires more plastering material and reduces carpet area by 25%. | Straight finished surface do not add up extra plastering materials and reduces carpet area by only 10-15%. |
| Brick walls are more prone to shrinkage cracks. | Dry walls do not experience shrinkage cracks. |
| Wet construction which is time consuming and involves curing at various stages. | Dry and fast construction and no curing needed. |
| Life of the building and durability using CFS framework. | Expected life span of 100 years or so whilst durability is subject to 'abuse by user'. |
| Waterproofing and patches on walls. | The method/material used and workmanship takes care of these issues. |
| External and internal finishes. | Treatment using 'stucco', tiles, stones, paints etc works well on the cladding and have cleaner lines than brick walls. |
| Hollow sound/sound transfer in wall structures. | Filling the cavity with Rockwool Insulation or CLC takes care of the STC, above the codes. Floor 'heel sound' transfer can be treated with usage of acoustic lining on floor before tiling. |
| Insulation leading to energy savings. | The infill material and has a substantial improvement over the brick wall. |
| Door and window finishes. | Better due to accuracy of openings. |
| USPs and weaknesses for DRY WALL Constructions. | Time factor and increase of carpet area being USP, whilst weakness is that designs need to be frozen before starting detailing and execution. |
| CFS framework construction more expensive than RCC construction. | Under present market prices, the direct construction costs are at PAR, but CFS could lead to a higher ratio of Carpet to built-up area. The Financial Interest burden of RCC construction because of time factor greatly reduces in CFS framework construction. |
LGSF Fully Integrated Construction process
Case 1: Rooftop Project
Project Area
1,200 sft
LGSF Quantity
2.8 MT (2.4 kg/sft)
Wall Composition
Outer Wall
8mm Fiber Cement Board + 10mm FCB Planks
Inner Wall
8mm FCB + 12.5mm Gypboard
Insulation
100mm / 64kg/m³ Rockwool
Roof
50mm PUF Sandwiched panel
Civil Work
Minimal (screed concrete)
LGSF + Foam Concrete vs Precast Concrete Housing
Comparison for Kalimantan Region (Kalimantan)
| Category | LGSF + Foam Concrete Housing | Precast Concrete Housing |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Construction Method | - Modular and lightweight - Minimal wet work - Easy to assemble with hand tools |
- Heavy concrete panels - Requires cranes and large lifting equipment - High logistics burden |
| 2. Speed of Construction | - 50–70% faster construction time - Prefabricated steel frames - Foam concrete poured on-site in 1 day |
- Slower due to curing and crane erection - Limited by joint works and wet weather delays |
| 3. Suitability in Heavy Rain | - Dry installation possible even during rain - Foam concrete is water-resistant and breathable - No curing required |
- Construction often delayed by weather - Joints vulnerable to water leakage and mildew |
| 4. Structural Quality | - Ductile and flexible under stress - No cracking due to foam absorption - High insulation value |
- Heavy and rigid structure - Prone to cracking at joints - Poor thermal insulation unless added |
| 5. Earthquake Resistance | - Lightweight and flexible - Absorbs seismic energy - Suitable for soft soils of Kalimantan |
- Heavy structure with rigid joints - Brittle under lateral movement |
| 6. Logistics & Accessibility | - Ideal for remote sites like Kalimantan - Flat-packed delivery via containers - Minimal heavy equipment needed |
- Bulky components difficult to transport - Requires wide access roads and handling cranes |
| 7. Manpower & Installation | - Semi-skilled labor sufficient after short training - Quick connections - Less supervision required |
- Skilled crane operators and riggers needed - More supervision required during joint sealing |
| 8. Cost Efficiency | - Lower foundation cost - Reduced transport and labor - Low maintenance over lifetime |
- High initial cost for transport and installation - Higher maintenance for waterproofing and cracking |
Why LGSF + Foam Concrete is Better for Kalimantan:
Built Faster: Erected in days, even during rainy seasons.
Transport Friendly: Light and modular — easy to ship by container or light trucks.
Rain-Proof: No wet curing delays; foam concrete resists mold and water.
Earthquake-Resilient: Withstands seismic activity common in Kalimantan.
Cost-Effective: Lower total cost due to reduced labor, transport, and long-term maintenance.
LGSF Housing with Foam Concrete Foundation
Higher in Quality
Faster in Speed
Enhanced Earthquake Resistance
Better Insulation
High Density Cellular Concrete Pavement
Methods, Methodology, Benefits, and Application
Introduction
- Foam Concrete: Lightweight concrete made by mixing cement paste with foam.
- High-Density Foam Concrete: Density range 1000–1800 kg/m³, structural use.
- Applications: Pavements, void filling, slope stabilization, etc.
Foam Concrete Pavement Benefits
- Reduced dead load on subgrade
- Excellent thermal insulation
- High workability and flowability
- Faster construction timelines
- Minimal shrinkage and settlement
Material Composition
- Cement: OPC or blended
- Foaming agent: Protein-based or synthetic
- Water: Potable
- Sand (optional): for >1400 kg/m³ density
- Additives: Plasticizers, retarders if needed